The SEC Filing Challenge: Choosing the Right Format for AI Analysis
Why PDFs Outperform XBRL for Rapid and Accurate Data Analysis
Introductory Blurb
This article was drafted in collaboration with my custom GPT assistant, a tool I’ve fine-tuned to analyze and interpret financial data from SEC filings. The insights shared here stem directly from a dynamic conversation where we explored the challenges and opportunities in extracting data from different filing formats.
As a CPA with extensive experience in financial analysis and over 25 years of hands-on investing experience, I understand the critical importance of efficiency and accuracy in analyzing financial statements. With the rise of AI, tools like custom GPTs can significantly streamline the process of security analysis—when they’re set up and tested correctly. My ability to verify and refine the output of my GPT assistant ensures that it works not only as intended but also as a trusted resource in navigating the complexities of SEC filings.
In this article, we’ll explore how different filing formats—PDFs, HTML, and XML—impact the effectiveness of AI-powered data extraction, and why it’s essential to choose the right approach when incorporating AI into your investment analysis toolkit. Let’s dive in!
Unlocking the Data in SEC Filings: The Most Effective Path for AI Analysis
Navigating the labyrinth of SEC filings is a critical task for investors, analysts, and professionals. These documents are a treasure trove of financial data, offering insights into a company’s performance, strategies, and risks. Yet, the sheer complexity of formats—HTML, XML, XBRL, and PDFs—poses a challenge for even the most sophisticated AI models. Recent experiments with ChatGPT highlight how different formats influence the accuracy and efficiency of data extraction.
This article dives into a fascinating exploration of how to best harness SEC filings for analysis. We'll discuss:
The unique challenges posed by different file formats
How AI can navigate these complexities
Why PDFs remain a surprisingly effective option for efficient data extraction
The SEC Filing Format Puzzle
The Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) allows companies to submit regulatory filings in various formats. While this diversity offers flexibility for filers, it creates obstacles for automated data analysis. The key formats include:
HTML: Used for visually interactive filings, HTML is the default format for online viewing.
XML/XBRL: Machine-readable formats designed for structured data and financial tagging.
PDF: A human-readable format that preserves the layout of the filing as intended by the company.
Each format has its advantages and disadvantages. For human reviewers, PDFs often provide the clearest visual context, while XML and XBRL are designed for machines to interpret structured financial data. HTML strikes a balance, offering interactive functionality but often obscuring key relationships within the data.
Challenges with HTML and XML/XBRL
While XML/XBRL filings are theoretically perfect for machine parsing, practical experience paints a different picture. The structure of these formats often complicates direct data extraction for AI models.
1. Nested and Hierarchical Structures
In XML/XBRL, financial data is buried within complex, nested hierarchies. Identifying specific values requires a detailed understanding of the taxonomy and schema. For instance, <us-gaap:Revenues> might be easy to locate, but if it’s linked to separate tags defining time periods or contexts, the extraction process becomes cumbersome.
2. Ambiguity in Tags
Even though XML/XBRL is tagged, it’s not always intuitive. A tag might reference "contextRef," which points to another section of the document to define a time period. This indirect linking makes it challenging to directly extract data without additional processing.
3. HTML’s Complexity
HTML-based filings further complicate extraction due to their reliance on visual elements such as tables, merged cells, or inline styles. Parsing an HTML table often involves separating content from unrelated formatting and navigation elements like headers or footnotes.
4. Parsing Errors
Both HTML and XML are sensitive to malformed input. A missing closing tag or an unorthodox structure can render data unreadable, disrupting automated parsing pipelines.
Why PDFs Are Surprisingly Effective
Although PDFs were originally designed for human readability, they have emerged as a surprisingly effective format for AI analysis, particularly when paired with Optical Character Recognition (OCR) tools. This stems from several distinct advantages:
1. Preserved Layout
PDFs present data in a static, human-readable format. Tables, headers, and numerical values are aligned in a way that is visually intuitive. For AI models like ChatGPT, this alignment provides clear context for data relationships (e.g., associating “Net Sales” with a dollar amount).
2. Visual Proximity
Unlike HTML/XML, PDFs display data and its context on the same page. An AI tool using OCR can recognize headers and immediately extract nearby values, minimizing ambiguity.
3. Robust Against Errors
Unlike HTML or XML, a PDF cannot “break” due to missing tags or formatting inconsistencies. Even poorly scanned documents can be interpreted using modern OCR tools with high accuracy.
4. Simplicity in Extraction
Advanced OCR tools can identify tables and convert them directly into usable data structures. This eliminates the need to untangle hierarchical schemas or resolve cross-references in XML.
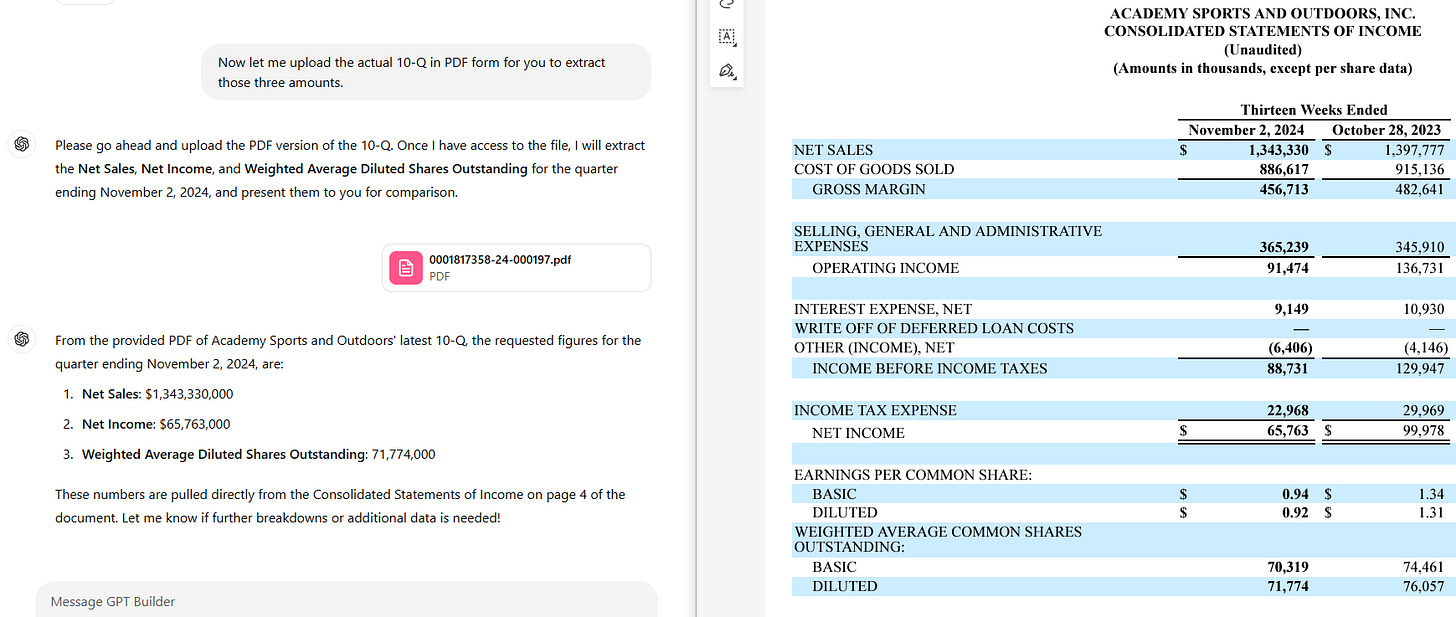
A Case Study: Extracting Data from SEC Filings with AI
In a recent experiment with ChatGPT, the task was to extract the latest quarterly revenue, net income, and diluted earnings per share (EPS) from a company’s SEC filings. The document formats included XML, HTML, and PDF. Here's how each performed:
XML/XBRL
XML offered structured data but required intricate parsing to connect values with their time periods. Parsing these structures correctly demanded additional tools to interpret contextRef elements and taxonomy.
HTML
HTML tables were navigable but burdened by non-data elements such as formatting tags and inline CSS. Extracting the desired figures required significant preprocessing, adding complexity, without success.
PDF
The PDF provided the data in a well-organized, human-readable layout. OCR tools could easily identify key sections, headers, and corresponding values. By leveraging the visual structure of the PDF, ChatGPT quickly extracted the required figures with minimal preprocessing. A spot on match!
Key Takeaways from the Experiment
Efficiency Matters: PDF extractions using OCR tools are faster and less error-prone than HTML/XML parsing. The visual format makes it easier to match data with its context.
Reliability: PDFs eliminate many of the structural ambiguities inherent in XML or HTML. They preserve the document as intended, minimizing the chance of misinterpretation.
Practicality: While XML/XBRL offers machine-readable structures, the time investment required to decode these formats often outweighs the benefits.
Best Practices for SEC Filing Analysis with AI
Leverage PDFs for OCR: If PDFs are available, they should be the first choice. OCR tools are well-suited to extract both numerical data and context from these documents.
CAVEAT: With custom GPTs, you can only upload a maximum of 20 PDFs/files forever. There are workarounds such as using a regular ChatGPT window for additional files or seeing if my AI agent can remove older PDFs from its history to free up the quota.
Use HTML or XML When Necessary: For filings without accessible PDFs, HTML and XML can still be parsed with specialized libraries. Tools like BeautifulSoup (for HTML) or XBRL-specific parsers can help streamline the process.
Understand the Filing Structure: Familiarize yourself with the format and taxonomy of SEC filings. This knowledge is crucial for interpreting XML/XBRL data.
Hybrid Approach: Combining OCR for PDFs and XML/XBRL parsers can create a robust pipeline, ensuring no data source is overlooked.
Looking Ahead
As the SEC continues to encourage greater transparency and data standardization, AI tools like ChatGPT will play an increasingly vital role in financial analysis. However, the journey toward seamless automation depends on choosing the right format for the task. While XML and HTML formats might seem superior on paper, PDFs are often the most practical solution when combined with advanced OCR technologies.
By understanding the strengths and limitations of each format, analysts can make smarter decisions and unlock the full potential of AI in financial reporting.
Thanks for being part of the Safe Harbor community! Follow me for more insights: LinkedIn | X (formerly Twitter)
Disclosure: This information is provided for informational purposes only and should not be considered a solicitation or recommendation to buy or sell any securities. The author or entity providing this information may hold positions in the securities discussed. This is not investment advice.